AI Unleashed: Your Guide to Navigating the Cyber World Ahead
Yep, it looks like the future marvels of Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology are here to stay. ChatGPT transforms machines into intelligent companions capable of composing a song about your dog in mere seconds. Here’s the catch: before you dive into the AI wonderland, it's crucial to understand the not-so-friendly security gremlins that might come along for the ride.
Imagine AI as your tech-savvy buddy—helpful, but a little mischievous at times. In this blog, we'll take you on a stroll through the AI park, pointing out the potential pitfalls of such technology and guiding you on how to keep your data safe. So, grab your virtual detective hat as we unravel the mysteries of AI security risks and how to sidestep them.
Choosing Your AI Chatbot Wisely
AI applications are in the limelight, and cyber criminals and attackers are quick to exploit the trend. Fake AI apps designed by malicious hackers or to deceive users into downloading them are on the rise. Vigilance is key to ensuring that the AI applications you employ are genuine and secure.
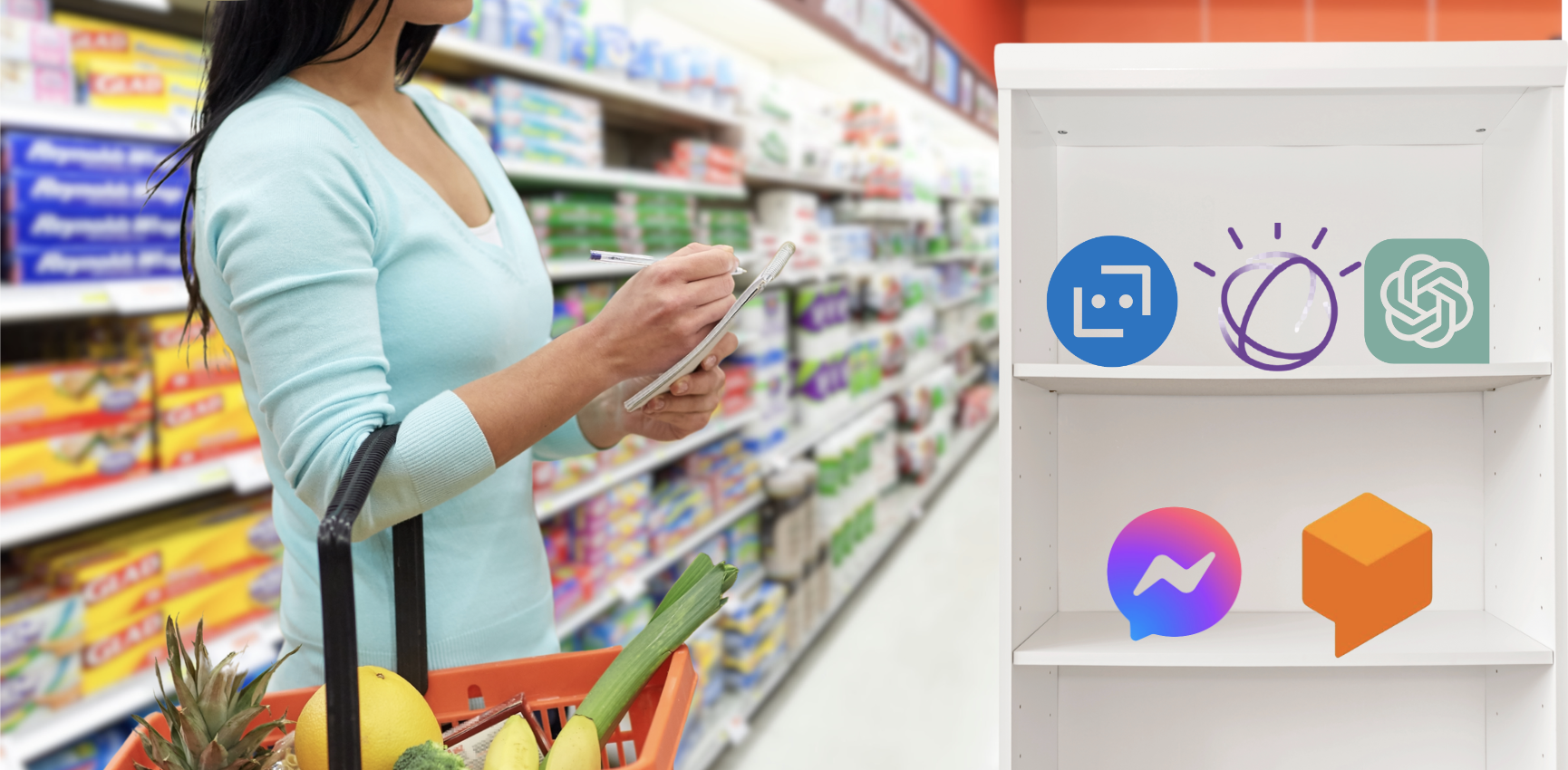

- ChatGPT:
- Functionality: Generates human-like text based on prompts.
- Pros:
- Versatile and can generate content on various topics.
- Easy to use; just type in prompts.
- Cons:
- Limited understanding of context.
- May produce inaccurate or biased content.
- Microsoft Azure Bot Service:
- Functionality: Develop and deploy intelligent bots.
- Pros:
- Integrates with the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Supports multiple channels (web, mobile, etc.).
- Cons:
- Requires technical knowledge for development.
- Limited to Microsoft platforms.
- IBM Watson Assistant:
- Functionality: Build AI-powered chatbots.
- Pros:
- Robust natural language processing.
- Integration with other IBM Watson services.
- Cons:
- Pricing can be high for extensive use.
- Requires some programming skills.
- Google Dialogflow:
- Functionality: Create natural language understanding applications.
- Pros:
- User-friendly interface.
- Strong integration with Google Cloud services.
- Cons:
- Can be complex for very specific tasks.
- Some advanced features may require coding.
- Facebook Messenger Bots:
- Functionality: Develop bots for Facebook Messenger.
- Pros:
- Large user base.
- Direct integration with Facebook pages.
- Cons:
- Limited to Facebook Messenger.
- Stricter policies on promotional content.
Choosing Your AI Chatbot: What to Consider?

- Purpose:
- Choose a chatbot aligned with your specific needs, whether it's customer support, lead generation, or general information.
- Ease of Use:
- Opt for a platform or service that matches your team's technical proficiency to ensure seamless integration and management.
- Scalability:
- Consider the potential growth of your operations and choose a chatbot that can scale with your business.
- Integration:
- Look for chatbots that easily integrate with your existing systems and tools to streamline processes.
- Cost:
- Evaluate the pricing structure of the chatbot platform and ensure it aligns with your budget, especially for long-term use.
Guarding Against Data Exposure
Understanding the Risks:
- Data Breaches: The unauthorized access and release of sensitive information, often due to cyber-attacks or system vulnerabilities.
- Insider Threats: Risks arising from within an organization, where employees or associates intentionally or unintentionally compromise data security.
- Best Practices for Data Protection:
- Data Encryption:
- What: Convert data into a code to prevent unauthorized access.
- Why: Safeguards information even if a breach occurs.
- Access Controls:
- What: Restricting access to data based on user roles and permissions.
- Why: Minimizes the risk of unauthorized data exposure.
- Regular Audits:
- What: Periodic assessments of data access and security protocols.
- Why: Identifies vulnerabilities and ensures compliance.
- Employee Training:
- What: Educating staff on data security practices.
- Why: Reduces the likelihood of human error leading to data exposure.
- Secure File Sharing:
- What: Using encrypted channels for sharing sensitive files.
- Why: Mitigates risks associated with data transmission.
Emerging Technologies for Data Security:
- Blockchain Technology:
- How: Utilizes decentralized and tamper-resistant ledgers.
- Benefits: Enhances data integrity and reduces the risk of unauthorized changes.
- AI-Powered Threat Detection:
- How: Analyzes patterns to identify potential data exposure threats.
- Benefits: Proactively detects and mitigates risks.
Real-World Scenarios:
- Equifax Data Breach (2017):
- Impact: Personal information of 147 million people was exposed.
- Lesson: The importance of robust security measures to prevent large-scale breaches.
- Insider Threat at Tesla (2021):
- Impact: Employees are leaking sensitive data.
- Lesson: Highlighting the need for comprehensive insider threat detection and prevention.
Caution in AI Photo Editors
Don't think we haven't forgotten about these guys. AI photo editors offer fun transformations, but uploading personal photos may pose privacy risks for users. Additionally, privacy concerns for users may arise about the use of uploaded photos for training facial recognition software. Exercise caution when using AI photo editors, considering the potential implications for your privacy.
Fact-Checking AI Information
AI tools are only as reliable as the data they use to create them. Inaccuracies, biases, or outdated information during data collection may compromise the output generated by a tool or AI. This applies not only to machine learning and content creation but also to coding, as programmers increasingly rely on AI tools to create them. To ensure the tool has accuracy and dependability, always verify the data that AI tools provide before incorporating it into your work.

Where AI Can Help and Hurt
Helpful:
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks:
- Facilitation: AI excels at automating mundane and repetitive tasks, enhancing efficiency, and allowing humans to focus on more complex endeavors.
- Example: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines data entry and processing.
- Enhanced Decision-Making:
- Facilitation: AI systems analyze vast datasets, providing valuable insights for informed decision-making across industries.
- Example: AI algorithms aid financial analysts in predicting market trends.
- Personalized Experiences:
- Facilitation: AI-driven personalization tailors user experiences in areas like online shopping, content recommendations, and social media interactions.
- Example: Recommendation algorithms on streaming platforms.
- Medical Advancements:
- Facilitation: AI contributes to medical research, diagnostics, and treatment, improving healthcare outcomes.
- Example: AI-assisted diagnostics in radiology.
Hurtful:
- Job Displacement:
- Complication: The automation of tasks by AI raises concerns about job displacement and the need for reskilling the workforce.
- Example: Automated assembly lines are replacing manual labor in manufacturing.
- Bias in AI Systems:
- Complication: AI algorithms may perpetuate and even amplify existing biases present in training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes.
- Example: Biased facial recognition algorithms impact certain demographic groups.
- Ethical Dilemmas:
- Complication: The use of AI in decision-making raises ethical concerns, especially in critical areas like criminal justice and autonomous vehicles.
- Example: Dilemmas around the ethical use of AI in predictive policing.
- Security Risks:
- Complication: AI systems are vulnerable to cyberattacks, and the misuse of AI poses security risks.
- Example: Deepfake technology creates convincing fake videos for malicious purposes.
Staying Defensive (And Up-To-Date)
It never hurts to stick with the same routine: avoid clicking links or downloading attachments from unfamiliar email addresses. Always verify requests from unknown sources through confirmed email addresses or phone numbers before taking any action.
In the dynamic realm of AI, understanding its potential and pitfalls is essential. By navigating the security risks thoughtfully and staying alert to emerging threats, individuals and organizations can harness the power of AI while safeguarding against potential dangers. Stay informed, stay cautious, and ensure that AI remains a trusted ally in your digital journey.






.png?width=1100&height=619&name=Super%20Blog%20Culture%20(1).png)
